How bio-based products and materials are promoting safety and reducing medical waste
How bio-based products and materials are promoting safety and reducing medical waste
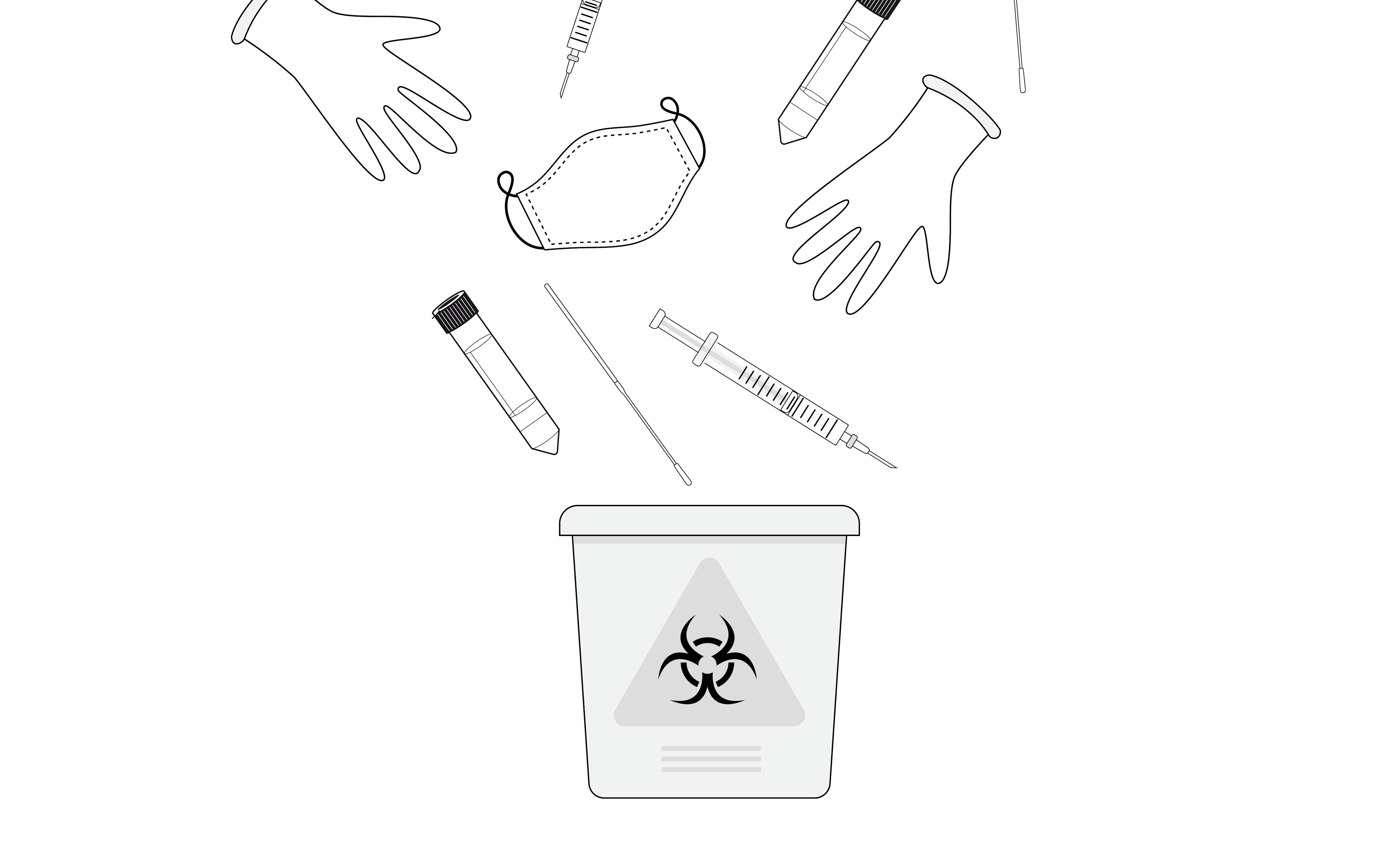
The Benefits of Disposable Medical Products
The healthcare industry is transitioning toward using more disposable products. Single-use products have a number of advantages over their reusable counterparts. They reduce the risk of contamination between uses and they tend to be more convenient. COVID-19, as well as other infectious diseases, can cause what are known as healthcare-associated infections or HAIs–in other words, infections that are passed to patients while they are receiving medical care inside a hospital environment. HAIs can have dire consequences and unfortunately they are fairly common. Around the world, it is estimated that 1.4 million patients are suffering from a healthcare-associated infection at any given time.1 Using disposable devices can significantly lower the risk of these infections.2 However, disposable medical products take a significant toll on the environment, generating millions of tons of waste each year. Medical products made from bio-based materials can offer the best of both worlds: the safety and convenience of a disposable product with a far lower environmental burden.
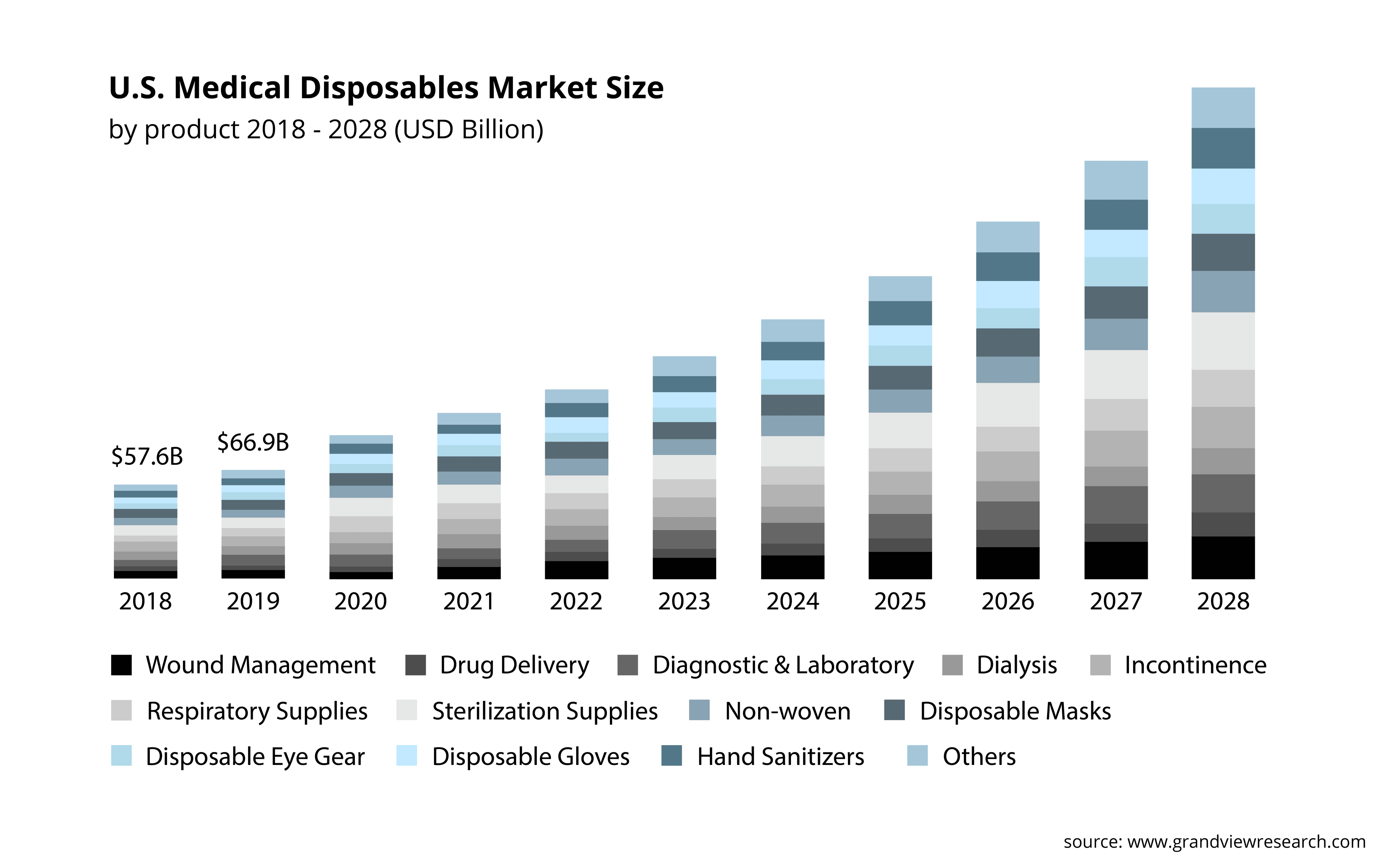
In the US, hospitals produce more than 5.9 million tons of medical waste every year. This doesn’t even include waste from medical offices, dental, veterinary, pharmacy, home care, and other arms of the healthcare industry which also generate medical waste.3 Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, this problem has become even more severe. For context, during the first year of the pandemic, more than 390 million COVID-19 testing kits were used in the US. Though these tests were a crucial part of mitigating the impact of the virus, they generated an immense amount of waste. Similarly, disposable masks, face shields, gloves, and other COVID-19-related disposable products are also piling up in landfills. Often this waste goes through various treatment processes, which can also have adverse effects on the environment.4 Incineration, the most common method for treating infectious disease waste, can release a variety of pollutants. This can cause serious public health issues such as higher incidences of cancer and respiratory problems, as well as environmental damage, like water and air pollution.5

Bio-Based Products Offer a Solution
Though the COVID-19 pandemic is not yet over, public health experts, scientists, doctors, lawmakers, and ordinary people have learned valuable lessons from this difficult time. We have Using bio-based, environmentally friendly materials to make medical supplies can be a way to cut down on the environmental and public health issues created by medical waste, without sacrificing the benefits of disposable supplies. Bio-based products are made of natural materials derived from organic sources including plants, sugar, and marine matter. These substances are versatile and can be used in various medical applications from wound care products to sampling devices.6 Bio-resins, for example, are resins derived from biological resources. Often these bio-resins can be blended with plastics to ensure that a device’s performance is not impacted, but its environmental footprint is lowered. At OPT, one of our polymers is 55% bio-derived, with material coming from coniferous trees. This polymer can be used to make high-performance, low-environmental impact medical products.
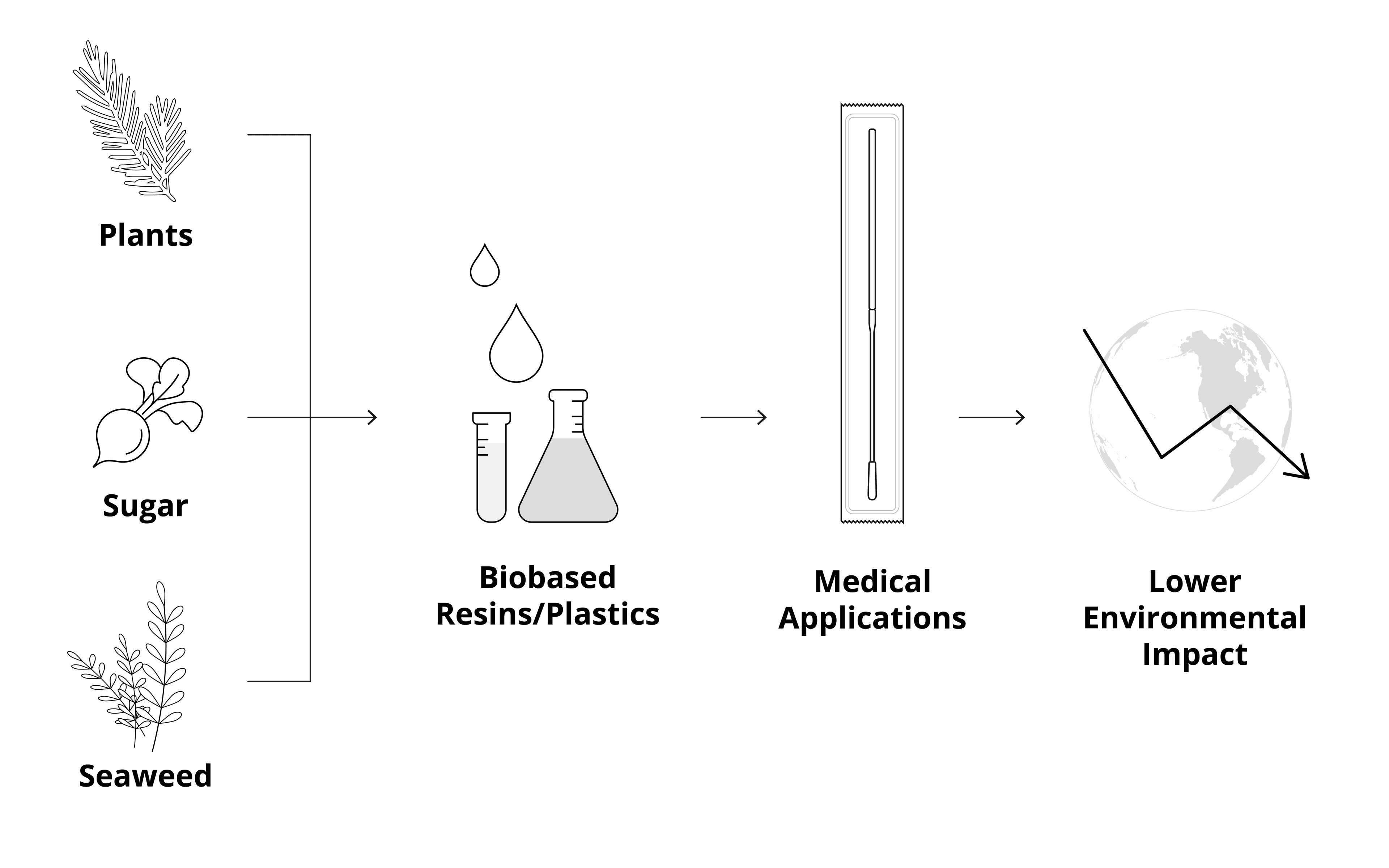
Unlike traditional medical waste, bio-based materials can be safely incinerated without releasing toxins or heavy metals which contaminate soil and plants, causing adverse health impacts for animals and humans as contamination moves up the food chain. This process is known as bio-accumulation.7
Many bio-based products are also degradable and compostable. As an example, compostable bio-resins can be completely converted into nutrient-rich biomass with no toxic byproducts.8 Some bio-based products can also be used for bioenergy. Biodegradable bioplastics can be collected and composted through bio-waste and this bio-waste can be used as either compost or renewable energy.9
Additionally, bio-based materials often require less energy during production than their traditional counterparts, which are derived from petroleum or natural gas.10 Generally, bio-based products have a lower carbon footprint from the beginning to the end of their lifecycle.
However, it is worth noting that some bio-based products can still cause harm to the environment if they are not handled properly. For instance, bio-plastics can be broken down into natural and non-toxic elements, but only if they are processed in a specific manner by industrial composting facilities.11 If they just end up in landfills, they can last for centuries and can release greenhouse gas, just like traditional plastic.11 Bio-based products have the potential to significantly reduce medical waste. However, collaboration between manufacturers, governments, waste processors, and other parties is necessary to truly unlock their environmental benefits.
Bio-based medical supplies are safe and prevent the spread of infections in hospitals because of their single-use nature. They also reduce medical waste, which will help preserve environmental health for future generations.
Bibliography
- The burden of health care-associated infection. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK144030/. Published 2009. Accessed July 1, 2021. “Around the world…1.4 million”
- Flowers N. Nature calls: The potentials of bioplastics within medical plastics – Medical Plastics News. https://www.medicalplasticsnews.com/medical-plastics-industry-insights/nature-calls/. Published 2018. Accessed July 1, 2021.
- Overstreet S. INFOGRAPHIC: 10 Things to Know About Medical Waste Compliance. https://blog.sharpsinc.com/10-things-to-know-about-medical-waste-compliance. Published 2016. Accessed July 1, 2021.
- Barndollar H. After COVID, another crisis: Medical waste from PPE, shots, testing. https://www.providencejournal.com/story/news/2021/04/08/covid-pandemic-medical-waste-disposal-crisis-ppe-testing-vaccine-equipment/4839287001/. Published 2021. Accessed July 1, 2021.
- Sharma R, Sharma M, Sharma R, Sharma V. The impact of incinerators on human health and environment. Rev Environ Health. 2013;28(1):67-72. doi:10.1515/reveh-2012-0035
- Thomas Publishing Company. Bioresins and Eco-friendly Plastics. https://www.thomasnet.com/articles/plastics-rubber/bioresin-plastics/. Accessed July 1, 2021.
- Bioplastics Guide. End of Life Options for Bioplastics. http://www.bioplastics.guide/ref/bioplastics/end-of-life-options. Accessed July 1, 2021.
- AllThings.Bio. How to dispose of bio-based plastics? https://www.allthings.bio/dispose-bio-based-plastics/. Accessed July 8, 2021.
- Eartheasy Guides & Articles. Bioplastics: Are They Really Better? https://learn.eartheasy.com/guides/bioplastics-are-they-really-better/. Accessed July 8, 2021.
- US Department of Energy. Bioproduct Basics. https://www.energy.gov/eere/bioenergy/bioproduct-basics. Accessed July 7, 2021.
- Robbins J. Why Bioplastics Will Not Solve the World’s Plastics Problem – Yale E360. https://e360.yale.edu/features/why-bioplastics-will-not-solve-the-worlds-plastics-problem. Published 2020. Accessed July 2, 2021.